Introduction to cationic light-curing monomers
-
Cationic photopolymerization mechanism
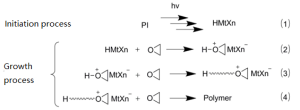
- Anaerobic polymerization resistance
- Less human irritation from epoxy monomer
- Less volume shrinkage
Better performance of polymerization product
Vinyl ether monomers
-
-
Classification of vinyl ether monomers
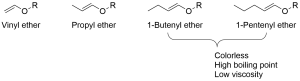
-
Vinyl ether-based monomers in market

Vinyl ether-based monomers in market -
Characteristics and applications of vinyl ether monomers
-
Characteristics:
- Very low viscosity
- High dilution capacity
- Low toxicity
- Very fast reaction time (comparable to acrylate monomer)
- Single structure. The stability of the product formed with vinyl ether monomer curing agent alone is poor
Application: Used as a cationic light-curing reactive diluent, not used alone
Epoxy propane monomer
-
Classification of Epoxy propane monomer
-
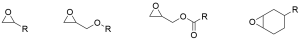
Classification of Epoxy propane monomer -
Epoxy propane monomer in market
-
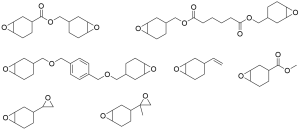
Epoxy propane monomer in market -
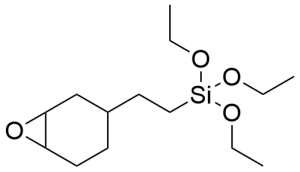
2-(3,4-Epoxycyclohexyl)ethyltriethoxysilane CAS 10217-34-2 - 2-(3,4-Epoxycyclohexyl)ethyltriethoxysilane CAS 10217-34-2
![Bis[2-(3,4-epoxycyclohexyl)ethyl]tetramethyldisiloxane CAS 18724-32-8](https://www.gmchemic.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Bis2-34-epoxycyclohexylethyltetramethyldisiloxane-CAS-18724-32-8-300x73.png)
Bis[2-(3,4-epoxycyclohexyl)ethyl]tetramethyldisiloxane CAS 18724-32-8 - Bis[2-(3,4-epoxycyclohexyl)ethyl]tetramethyldisiloxane CAS 18724-32-8
-
Characteristics and applications of epoxy propane monomer
Characteristics for Glycidyl ether epoxy monomer
- Longer induction period for cationic light curing
- Low cationic light-curing activity
- Unsatisfactory performance of the product
Characteristics for Alicyclic epoxy monomers
- Lower viscosity
- Fast cationic light curing speed
- Excellent performance of the product
- Less variety of products, large differences in curing activity between products
Oxetane monomers
-
Classification of Oxetane monomers
-

Classification of Oxetane monomers -
Oxetane monomers supplied by our company
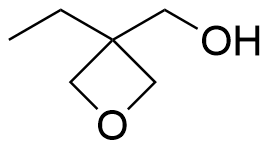
- 3-Ethyl-3-(hydroxymethyl)oxetane CAS 3047-32-3
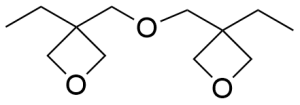
- 3,3′-(oxydimethanediyl)bis(3-ethyloxetane) CAS 18934-00-4
- 3,3′-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(4,1-phenyleneoxymethyl)] CAS 105071-04-3
![3,3′-[(1-methylethylidene)bis(4,1-phenyleneoxymethyl)] CAS 105071-04-3](https://www.gmchemic.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/33′-1-methylethylidenebis41-phenyleneoxymethyl-CAS-105071-04-3-300x58.png)
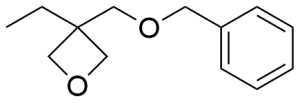
- 3-Ethyl-3-(phenylmethoxymethyl)oxetane CAS 18933-99-8
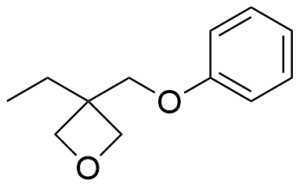
- 3-Ethyl-3-(phenoxymethyl)oxetane CAS 3897-65-2
- 1,4-Bis[(3-ethyl-3-oxetanylmethoxy)methyl]benzene CAS 142627-97-2
![1,4-Bis[(3-ethyl-3-oxetanylmethoxy)methyl]benzene CAS 142627-97-2](https://www.gmchemic.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/14-Bis3-ethyl-3-oxetanylmethoxymethylbenzene-CAS-142627-97-2-300x65.png)
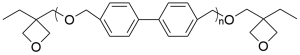
- 4,4′-Hydroxymethylbiphenyl polymer oxetane CAS 358365-48-7
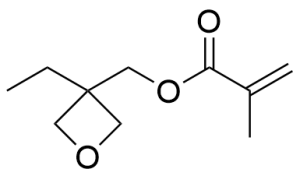
- 3-Ethyl-3-methacryloxymethyloxetane CAS 37674-57-0
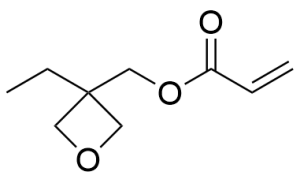
- (3-Ethyl-3-oxetanyl)methyl acrylate CAS 41988-14-1
- 3-Ethyl-3-[[3-(triethoxysilyl)propoxy]methyl]oxetane CAS 220520-33-2
![3-Ethyl-3-[[3-(triethoxysilyl)propoxy]methyl]oxetane CAS 220520-33-2](https://www.gmchemic.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/3-Ethyl-3-3-triethoxysilylpropoxymethyloxetane-CAS-220520-33-2-300x110.png)
Characteristics and applications of oxetane-based monomers
Characteristics:
- Low curing volume shrinkage
- Low viscosity
- Low toxicity
- Fast reaction speed
- Ability to frontline polymerization and delayed curing
- Good performance of polymerization products
-
Influencing factors of cationic light curing
- Nucleophilic/basic substances
- The effect of temperature. During curing, the higher the temperature the faster the curing speed. (pre-baking, post-baking, self-produced heat)
- Effect of water/moisture. A small amount of water speeds up the curing process, and as the water content and humidity increase, cationic curing is inhibited.
- The effect of alcohol. Chain transfer agent that speeds up cationic light curing but reduces the molecular weight of the polymer.
- The effect of viscosity. The higher the viscosity of the formulation, the slower the reaction rate.